Carotid Cavernous Fistula & Artery Stenting Treatment
Carotid Artery Stenting Treatment offered by Dr. Kalpesh Shah
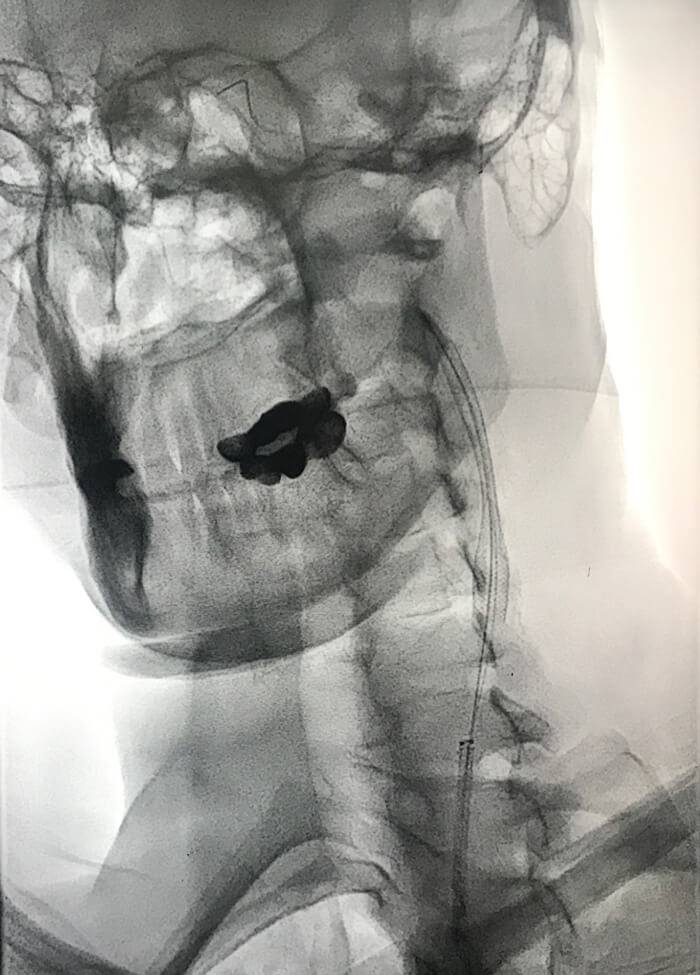
Carotid artery stenting is a medical procedure used to treat carotid artery disease. It involves the placement of a stent, a small mesh-like tube, within the carotid artery to open up a narrowed or blocked section and restore normal blood flow to the brain. Carotid artery disease occurs when the carotid arteries, which are located on each side of the neck, become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of plaque. Plaque is composed of cholesterol, fat, calcium, and other substances that accumulate on the inner walls of the arteries; a condition known as atherosclerosis.
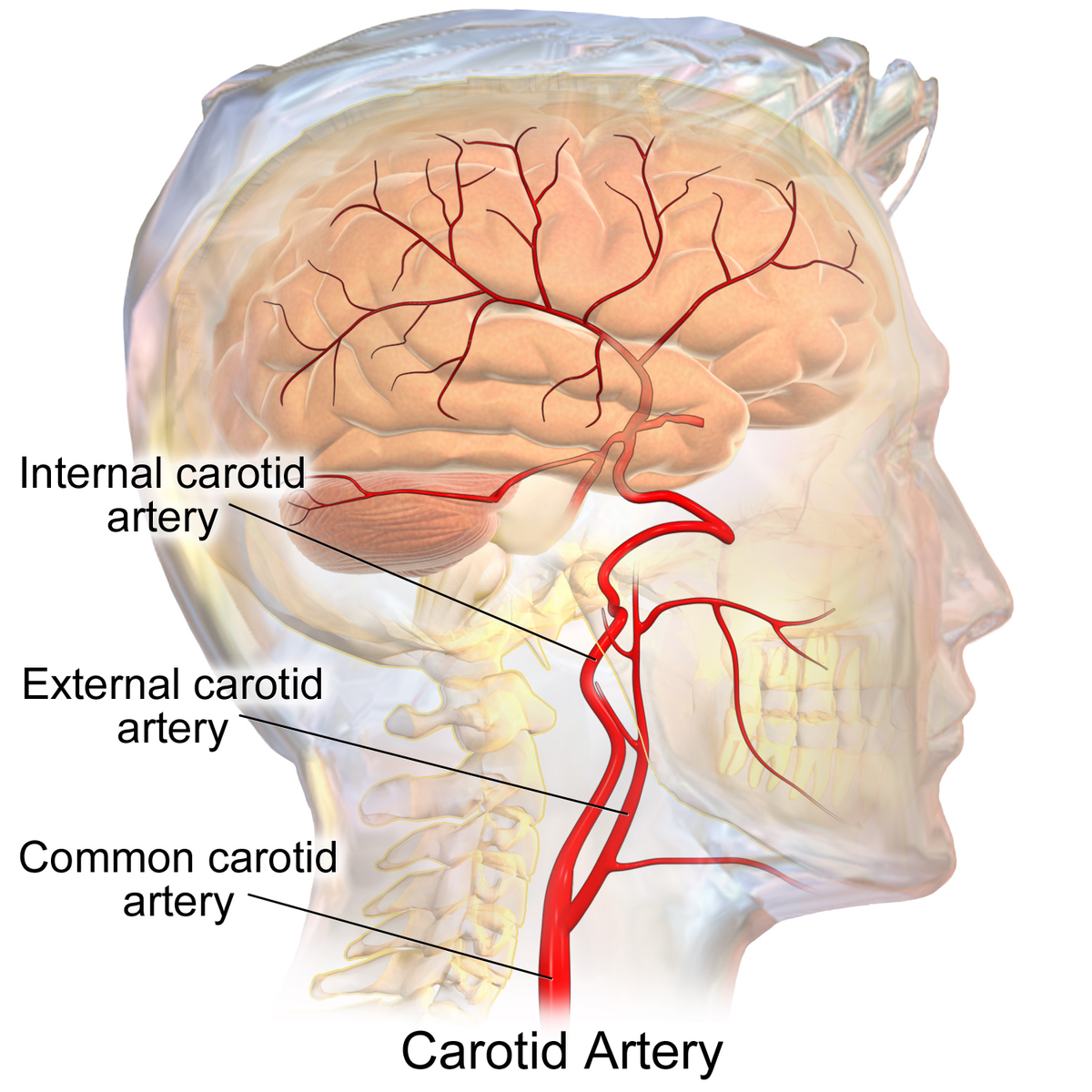
Causes of Carotid Artery Stenting
Carotid artery stenting is primarily performed to treat carotid artery disease, which is caused by the buildup of plaque within the carotid arteries. Plaque is composed of cholesterol, fat, calcium, and other substances that accumulate on the inner walls of the arteries, narrowing the blood flow. This condition, known as atherosclerosis, can lead to serious health risks such as stroke or transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) if left untreated.
Symptoms of Carotid Artery Stenting
Carotid artery disease often presents with little to no symptoms in its early stages. However, as the condition progresses, individuals may experience:
- Transient ischemic attacks (TIAs): Also referred to as "mini-strokes," these episodes typically last for a few minutes and may cause temporary weakness, numbness, or speech difficulties.
- Stroke: A severe manifestation of carotid artery disease, strokes can lead to long-lasting neurological deficits, including paralysis, difficulty speaking, and loss of coordination.
- Carotid bruits: Unusual sounds or murmurs heard over the carotid arteries during a physical examination may indicate the presence of significant blockages.
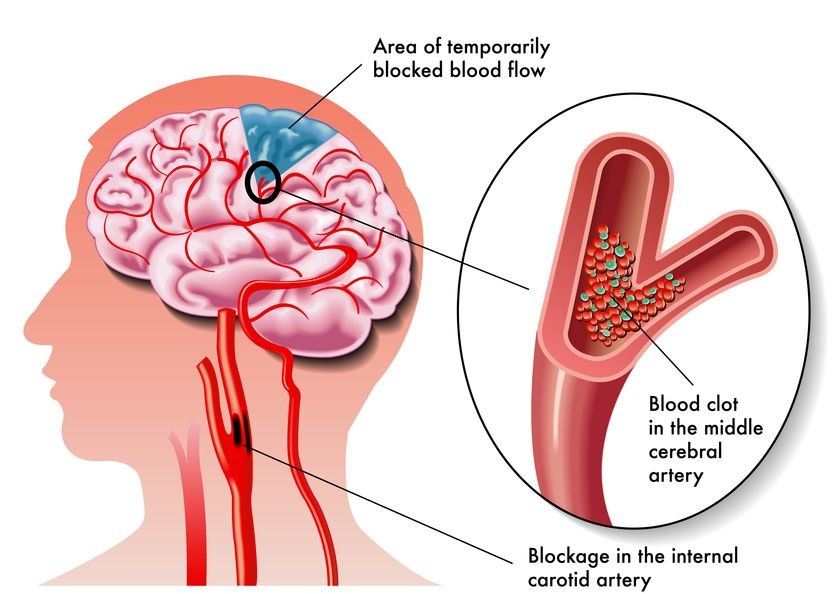
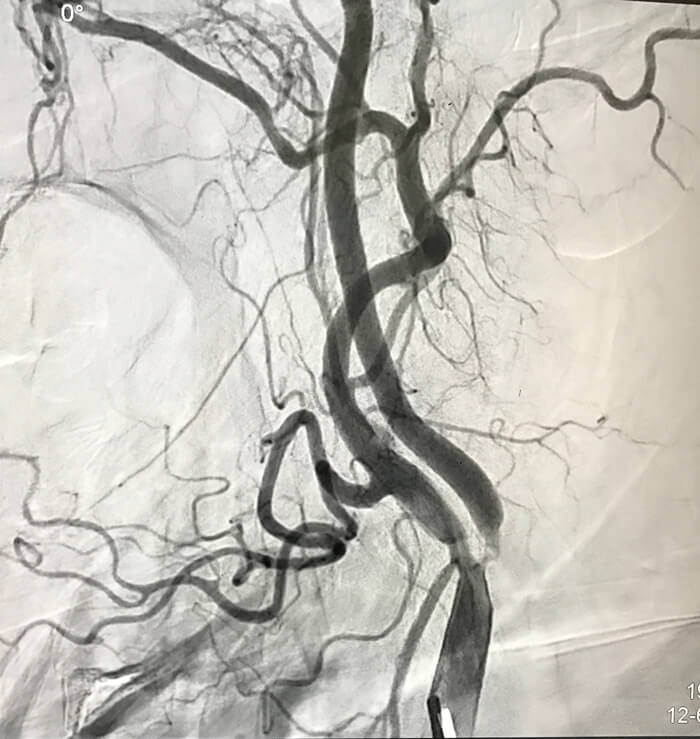
Diagnosis of Carotid Artery Stenting
If carotid artery disease is suspected, your doctor may recommend the following diagnostic tests:
- Carotid ultrasound: This non-invasive imaging technique uses sound waves to create detailed images of the carotid arteries, helping to determine the extent of blockages.
- Doppler ultrasound: By measuring the blood flow through the carotid arteries, this test can identify any abnormalities in circulation.
- Angiography: A more invasive procedure, angiography involves injecting a contrast dye into the arteries and using X-rays to visualize any blockages or narrowing.
- Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA): This imaging technique utilizes magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of the blood vessels, providing information about the blood flow and potential blockages.
Treatment options for Carotid Artery Stenting
The primary goal of carotid artery stenting is to restore normal blood flow to the brain and prevent the occurrence of strokes or TIAs. The procedure involves the following steps:
- Preparing the patient: Prior to the stenting procedure, the patient is usually given medications to prevent blood clotting and sedation to help them relax.
- Accessing the artery: A small incision is made in the groin area, through which a catheter is inserted into the femoral artery.
- Guiding the catheter: The catheter is threaded through the arteries until it reaches the site of the carotid artery blockage.
- Placing the stent: A stent, a small mesh-like tube, is then positioned in the narrowed segment of the carotid artery to expand and support the vessel, facilitating improved blood flow.
- Recovery and monitoring: Following the procedure, patients are closely monitored to ensure there are no complications, and medications may be prescribed to manage any underlying conditions, such as high blood pressure or cholesterol.
It’s important to note that carotid artery stenting may not be suitable for all patients. Your doctor will carefully evaluate your specific condition and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual factors. If you have any concerns or questions regarding carotid artery stenting or any other medical condition, please consult with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Play Video
Risks and Complications:
While carotid artery stenting is generally considered a safe procedure, there are potential risks and complications that may arise. These can include:
- Stroke: There is a small risk of stroke during or after the procedure, particularly if plaque or blood clots dislodge and travel to the brain.
- Infection: Any invasive procedure carries a risk of infection at the site of the incision or in the blood vessels.
- Bleeding: There is a possibility of bleeding at the incision site or along the catheter's pathway.
- Allergic reactions: Some individuals may have an allergic reaction to the contrast dye used during angiography.
- Restenosis: In some cases, the carotid artery may become narrowed again (restenosis) after the stenting procedure, requiring further intervention.
It is important to discuss these risks with your healthcare provider before undergoing carotid artery stenting.
Post-Procedure Care
After carotid artery stenting, it is crucial to follow the recommended post-procedure care instructions provided by your healthcare team. These may include:
- Rest and recovery: Take it easy for a few days following the procedure, avoiding strenuous activities.
- Medications: Your doctor may prescribe medications to prevent blood clotting, lower cholesterol levels, or manage blood pressure.
- Regular follow-up visits: Schedule follow-up appointments to monitor your progress, assess the effectiveness of the stenting procedure, and adjust medications if necessary.
- Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help manage carotid artery disease and reduce the risk of further complications. This includes eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, quitting smoking if applicable, and managing underlying conditions such as diabetes or hypertension.
It’s important to note that carotid artery stenting may not be suitable for all patients. Your doctor will carefully evaluate your specific condition and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual factors. If you have any concerns or questions regarding carotid artery stenting or any other medical condition, please consult with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized advice.